- Texas Medical Cannabis Dispensaries vs Hemp Stores
- 5 Easy Steps to Fill Your Prescription
- Decoding Texas Cannabis Ratios: 20:1, 1:1, 0:1…
- Dosing & Product Education
- Texas CUP News & Legislation
- Conditions & Symptom Relief
- Practice Updates & Patient Stories
- Caregivers & Family Support
- Compliance & Legal FAQs
- Texas Medical Cannabis Guidebook 📚
- Complete Learning Library 📚
Cannabinoid Science
Medical Cannabis in Texas: Science, Safety & Legal Access
medical cannabis texas
“Explore the therapeutic potential of medical marijuana with FloweretMD Medical Cannabis Clinic. From treatment options to patient success stories, discover how medical marijuana can improve quality of life.”cannabis
Ready for legal relief? Schedule a risk-free online visit and see if you qualify for a Texas medical marijuana prescription today.

Medical Cannabis Overview
Over the past decade, medical cannabis in Texas and across most U S states has shifted from taboo to treatment as more legislatures pass patient-focused laws. Yet many people—including clinicians—still lack clear insight into cannabinoid science and the practical steps for securing a Texas medical marijuana prescription. That knowledge gap is especially wide here in Texas, where fewer than 1 % of physicians are authorized to enter patients into the Compassionate Use Program (CUP).
Floweret MD Medical Cannabis Clinic bridges that gap. Our board-certified team delivers non-biased, research-backed guidance on THC, CBD, and the broader endocannabinoid system so patients and caregivers can make confident choices—whether they’re brand-new to cannabis or meeting with a medical marijuana doctor online for ratio adjustments.
In this section you’ll learn:
Key therapeutic cannabis compounds (THC, CBD, CBN, CBG)
How the endocannabinoid system (ECS) regulates pain, mood, and sleep
Evidence-based benefits of low-THC cannabis for Texas patients
Step-by-step access to legal medical marijuana in Texas through CUP
Current state and federal laws governing safe, compliant use
By the end, you’ll understand how legal, physician-guided cannabis can fit into your care plan—and exactly how to get started.
Cannabinoids
The prized chemical compounds found in cannabis are known as cannabinoids. These compounds are similar in structure to the endocannabinoids naturally produced in our bodies. There are over 140 different cannabinoids in the cannabis plant.
We will stick to the most notable, THC and CBD. Still, it is essential to understand that cannabis flowers contain a plethora of cannabinoids, such as CBG, CBN, CBC, THCA, and THCV, each with unique properties. While we have much to learn about the ‘minor cannabinoids,’ their future medical applications look promising.


Terpenes
The other essential compounds found in cannabis are terpenes. Like cannabinoids, these plant oils are located in the plant’s resin glands on the buds, flowers, leaves, and even to a lesser extent on the stems. Terpenes are found in all plants and are typically used to protect the plant or attract pollinators. They are vital to the plant’s survival and evolution.
Terpenes have been used in folk medicine for thousands of years, each providing a unique assortment of benefits. While over 20,000 terpenes have been identified, there are about a dozen produced in cannabis. These plant oils assist the cannabinoids in delivering flavor, color, and therapeutic remedies. They also alter the user experience. Types of cannabis with high concentrations of sedating terpenes like myrcene are believed to be responsible for the tranquil effects of Indica-dominant cannabis strains. Conversely, terpenes like pinene deliver uplifting effects and are commonly found in Sativa-dominant strains.
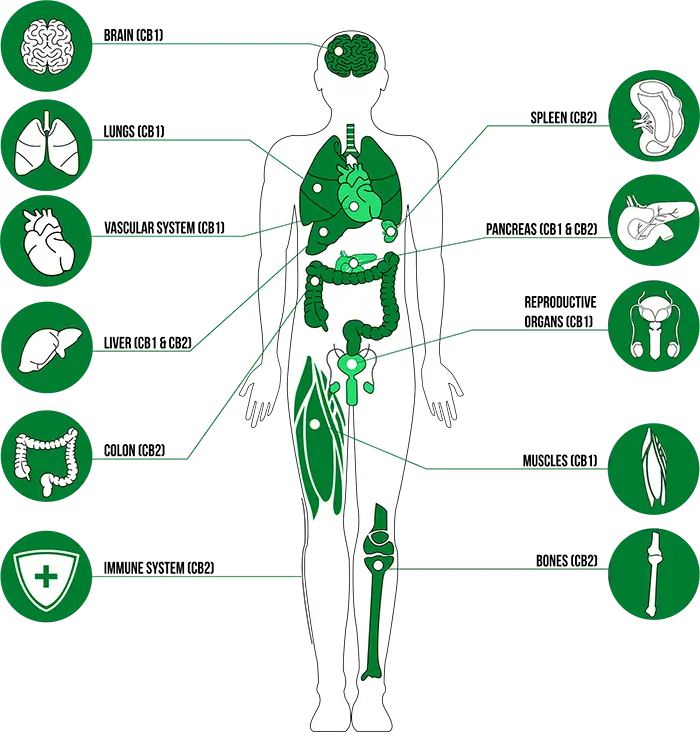
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
Our body contains a complex cell-signaling network that works to maintain balance through the body. This network is known as the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system consists of the following main components:
Endocannabinoids – Compounds very similar in structure to plant-based cannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are neurotransmitters, sending complex messages throughout the ECS.
Endocannabinoid Receptors – Located throughout the body, primarily found in the brain, central nervous system, and spleen; Responsible for regulating several bodily functions such as mood, appetite, memory, inflammation, anxiety, and the sleep-wake cycle.
Enzymes – Proteins that can increase or decrease the production of endocannabinoids.
The endocannabinoid system functions to maintain balance within the body despite fluctuations in the external environment. The endocannabinoid system was discovered in 1988 when scientists at the St. Louis University School of Medicine were studying cannabis’s effects on the body. They found that the brain of mammals contained receptors that respond to compounds from cannabis. These receptors were referred to as CB1 receptors and, remarkably, found to be the most abundant neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. In addition, another cannabinoid receptor (CB2) was identified during the study. With the discovery of the CB2 receptors in the immune system and peripheral nervous system, scientists were able to isolate compounds in our body structurally similar to cannabis-based cannabinoids. Therefore, they named them endocannabinoids from the root word “endo,” meaning internal or inside.
The ECS produces endocannabinoids when there is an imbalance in our body. These endocannabinoids interact with the cannabinoid receptors to perform tasks such as minimizing the stress response, reducing inflammation, decreasing pain, relaxing tense muscles, stimulating appetite, modifying the sleep cycle, producing relaxation, and elevating mood.
Hemp vs. Marijuana
Both hemp and marijuana come from the Cannabis sativa plant, yet their legal and medical roles in medical cannabis Texas differ sharply. Any Cannabis sativa containing only 0.3 % THC or less is classified as hemp—often labeled “low-THC cannabis” in Texas statutes—while plants with higher THC levels are treated as marijuana and fall under the Compassionate Use Program Texas. Hemp’s naturally higher CBD content makes it popular for over-the-counter oils, but its THC is too low to deliver the balanced CBD : THC ratios many patients need for the full benefits of medical cannabis.
Because hemp products are sold online or at gas-station retailers, they lack the testing safeguards required for a Texas medical marijuana prescription. Lab studies often show CBD or THC levels that don’t match the label, and the industry has minimal oversight. By contrast, products dispensed through a medical marijuana doctor online or in-clinic follow strict CUP regulations—ensuring accurate dosing, contaminant screening, and consistent relief. Texas may still be restrictive compared with other states, but its tighter rules guarantee higher quality and safety for patients seeking medically guided cannabis therapy.
Thinking about safe, legal relief? Schedule a quick, no-pressure telehealth visit with Floweret MD Medical Cannabis Clinic and learn whether a Texas medical marijuana prescription is right for you.

Medical Benefits of THC
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is notorious for its psychoactive effects, but it also has medical applications that can be life-changing. THC is similar in structure to our body’s endocannabinoids. This similarity allows THC to attach to cannabinoid receptors throughout the body, activating the same responses as our internal endocannabinoid system. As a result, people suffering from a wide range of medical conditions, including but not limited to pain, muscle spasticity, glaucoma, insomnia, low appetite, nausea, seizures, myoclonus, Crohn’s disease, neuropathy, ALS, Lupus, interstitial cystitis, anxiety, PTSD, and cancer, have reported relief while using medical cannabis.
THC increases effectiveness and minimizes side effects when used alongside other traditional drugs. For instance, cancer patients use medical cannabis to combat the adverse effects of chemotherapy. THC can increase the appetite, reduce pain, and help the patient sleep while undergoing treatments.
A few pharmaceutical drugs feature THC as the active ingredient; the most notable is called Sativex. The Sativex spray contains a full array of cannabinoids with varying amounts of THC. Many countries have approved the drug to treat Multiple Sclerosis (MS); in the USA, Sativex is currently in clinical trials in the US.
One of the most exciting aspects of medical marijuana is its potential to reduce pain without life-threatening side effects. The US is faced with an increasing number of opioid overdoses, partly due to the addictive properties of drugs that treat pain. Data shows that access to cannabis directly translates to lowing overdoses in specific areas.
CBD Basics
CBD (cannabidiol), the second most prevalent plant-based cannabinoid, is derived from hemp. CBD gained notoriety for its therapeutic benefit on rare childhood seizure conditions, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS). These conditions usually do not respond to antiseizure medications. Yet, CBD was decreasing the frequency of those seizures and, for some, eliminating seizures. In 2018, Epidiolex became the first plant-derived cannabinoid prescription medicine and the only FDA-approved form of CBD for use in these conditions.
CBD doesn’t have the affinity to bind with receptors in the brain, making an intoxicating reaction impossible. Evidence suggests that CBD also reducing THC’s ability to bind to receptors in the brain, thereby reducing the psychoactive effects of THC while allowing the therapeutic effects to remain. Benefits of CBD cross over with THC, though the responses may differ. For instance, CBD has milder pain relief properties than THC, while CBD tends to have more anti-inflammatory action. Still, CBD has been used to treat the following:
- Seizures
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Psychosis or mental disorders
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Nausea
- Migraines
- Depression
- Anxiety

Medical Marijuana in Texas
Texas established the Compassionate Use Program in 2015 for patients with specific qualifying conditions. In 2019, the 86th Texas Legislature expanded the program to include more qualifying conditions. On June 15, 2021, Governor Abbot signed House Bill 1535, expanding the program further to include PTSD and all cancer beginning September 1, 2021, and doubling the percent by weight of THC allowed in medical cannabis products from 0.5% to 1%.
To qualify, Texas residents must have a qualifying condition and receive a prescription from a doctor. If you are under the age of 18, you need a legal guardian or caregiver.
Outside of Texas?
*Our network of licensed physicians can also provide prescriptions to patients in the following states: California, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, and Rhode Island. Qualifying conditions vary by state. Use the chatbox or register through the patient login to be connected to your state’s specialist.
Qualifying Conditions in Texas
HouseBill 46 goes into effect September 1, 2025, and will add more conditions. See bottom of list.
- ALS,
- Alzheimer’s Disease,
- Autism,
- Cerebral Palsy,
- Chronic Traumatic Brain Encephalopathy,
- Epilepsy and other Seizure disorders,
- Huntington’s Disease,
- Multiple Sclerosis,
- Muscular Dystrophy,
- Parkinson’s Disease,
- Peripheral Neuropathies,
- PTSD
- Muscle Spasms/Spasticity,
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy,
- Terminal Cancer (all cancers-new law begins 9/1/2021)
- for full list of Incurable Neurodegenerative Diseases.
- A condition that causes chronic pain (Sept 1, 2025)
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI) (Sept 1, 2025)
- Crohn’s disease or other inflammatory bowel disease (Sept 1, 2025)
- A terminal illness or any condition for which the patient is receiving hospice or palliative care (Sept 1, 2025)
Take the Next Step Toward Powerful Relief. Connect with a Texas-licensed medical cannabis doctor and secure your Texas medical marijuana prescription from the comfort of home.
Get a Little Closer
Subscribe
Sign up to get the latest information on sales, new releases, and more…


